FW
"As per, in 2017, the United States with €631 billion (16.9 per cent) and China €573 billion (15.3 per cent) continued to be the two main goods trading partners of the European Union (EU), well ahead of Switzerland (€261 billion,), Russia (€231 billion), Turkey (€154 billion) and Japan (€129 billion). These figures reflect an interesting proposition. After recording significant and almost continuous fall until 2011, the share of the United States in EU total trade in goods has increased nearly 18 per cent in 2015 and 2016, before decreasing again slightly in 2017."
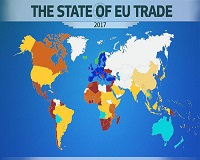
As per, in 2017, the United States with €631 billion (16.9 per cent) and China €573 billion (15.3 per cent) continued to be the two main goods trading partners of the European Union (EU), well ahead of Switzerland (€261 billion,), Russia (€231 billion), Turkey (€154 billion) and Japan (€129 billion). These figures reflect an interesting proposition. After recording significant and almost continuous fall until 2011, the share of the United States in EU total trade in goods has increased nearly 18 per cent in 2015 and 2016, before decreasing again slightly in 2017.
China’s share almost tripled since 2000, rising from 5.5 per cent to 15.3 per cent in 2017. Russia’s share had been decreasing since 2012 from nearly 10 per cent to around 6 per cent in 2016, and picked up a little in 2017. The share of trade with Japan has fallen more than half since 2000 from 7.5 per cent in 2000 to 3.5 per cent in 2017. As for Switzerland and Turkey, their respective shares in trade remained relatively unchanged over the entire period. In 2017, machinery and transport equipment, other manufactured goods and chemicals represented the main categories of product traded by the EU.
Favoured export destinations

In almost all EU Member States, the main partner for goods exports in 2017 was another EU member, except for Germany, Ireland, and the UK (the United States was the main destination of exports) for Cyprus it was Libya and for Lithuania, Russia. In some member states, over a quarter of exports went to one single partner. This partner was Germany for the Czech Republic (33 per cent of exports of goods), Austria (29 per cent), Hungary (28 per cent), Poland (27 per cent) and Luxembourg (26 per cent). Around 27 per cent of Ireland’s exports went to the US and 25 per cent from Portugal went to Spain. Overall, Germany was the main destination for goods exports for 17 Member States and among the top three in 22 Member States. For extra-EU trade, that is trade with non-EU countries, the 3 main destinations of EU exports in 2017 were the US (20 per cent of all extra-EU exports), China (11 per cent) and Switzerland (8 per cent).
In 2017, the 28 EU Member States exported a total of € 5,226 billion of goods, of which €3,347 billion (or 64 per cent) were destined for another Member State of the EU (intra-EU trade). With about three-quarters or more of goods exported to other EU Member States, Slovakia (86 per cent intra-EU in total exports), Luxembourg and the Czech Republic (both 84 per cent), Hungary (81 per cent), Poland (80 per cent), Romania and Slovenia (both 76 per cent) and the Netherlands (75 per cent) recorded in 2017 the highest shares of intra-EU exports. At the opposite end of the scale, Cyprus (37 per cent) and the United Kingdom (48 per cent) were the only Member States that exported more goods to non-EU countries than within the EU in 2017.
Import scenario
The main partner for goods imports in 2017 was another member of the European Union in all Member States except Lithuania, for which Russia was the main country of origin of goods imported, and the Netherlands (China). In seven Member States, more than 25 per cent of imports were from a single partner country in 2017: Austria (42 per cent of imports of goods originated from Germany), Luxembourg (32 per cent from Belgium), Portugal (32 per cent from Spain), the Czech Republic (30 per cent from Germany), Ireland (29 per cent from the UK), Poland (28 per cent from Germany) and Hungary (26 per cent from Germany). Overall, Germany was among the top three countries of origin of goods imported in all EU Member States except Ireland and Cyprus. For extra-EU trade, the main country of origin of goods imported into the EU in 2017 remained China (20 per cent of all extra-EU imports), followed by the US (14 per cent) and Russia (8 per cent).
Ethiopia has over 2.4 million hectares of land are suitable for cotton production. And this fiscal, over 40,000 tons of cotton were harvested. The aim is to reach 5,02,000 tons in five years and 2,596,000 tons by 2032.
Ethiopia wants to be the top cotton producer in Africa from tenth place as of now. Sustainable production practices will be promoted through awareness raising campaigns about soil erosion, efficient use of irrigation water and inputs and integrated pest management, protection of biodiversity, forests and limitation of waste.
The strategy would help enhance the development of the country’s textile and garment sector. It is targeted to attain various goals including improving textile and garment products, earning better foreign currency, job creation, utilizing the full potential of industry and increasing the contribution of the industry for GDP. It would also contribute to attracting investments, providing adequate inputs for industries and supplying cotton products for foreign markets.
The strategy would promote integrated value and help bring the cotton sector into the industrialization process and will benefit all stakeholders in general and cotton farmers in particular as it would make them more profitable. An independent entity will be established with authority to coordinate activities by various stakeholders through improving policy and institutional framework.
Industry 4.0 poses a challenge to Vietnamese labor force. The country will struggle to adapt to Industry 4.0—the wave of rapid technological development transforming workforces and economies across the world.
For example, 86 per cent of workers in Vietnam’s textile and footwear industries are at great risk of losing their jobs under the influence of technological breakthroughs caused by Industry 4.0. Industry 4.0 will leave no place for farming workers. The youth unemployment rate will be higher. The shortage of skilled workers as Industry 4.0 comes will also be very high.
Among the 100 countries assessed, Vietnam was ranked among those that aren’t ready for Industry 4.0. More than half of Vietnam’s workforce is under the age of 40, with the proportion of workers aged 15 to 29 at 25 per cent. Not only lacking in professional knowledge, Vietnamese workers are weak in problem solving, leadership and communication skills. The quality of education and skills of staff, especially engineers and technicians, are below par. The advantage of low labor costs in Vietnam is gradually losing attractiveness in the eyes of foreign investors.
Training institutions need to adopt learner-centered training methods and the application of information technology in lecture design and delivery.
Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality is the first plant in Turkey that produces yarn completely out of recycled plastic bottles. Having started as a family firm in 2009, IBB exports to 20 countries. Plastic bottles used by the company are collected from several locations, such as schools, hospitals, hotels and various institutions, and then processed in fiber.
Turkey has pioneered recycling efforts in recent years, both through awareness initiatives to empower individual consumers and also recycling infrastructure to take advantage of the resources discarded in the trash. Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality aims to increase the volume of renewable waste collected from people through a new system that will refund the value of each recycling deposit to the resident's megacity transport card.
Increasing yarn production contributes to the Turkish economy. The yarn, which is internationally-accredited and certified, is not produced using conventional methods. In a feat of process engineering, IBB has used self-developed knowhow to transform plastic waste into fiber and yarn. IBB’s daily production capacity is five tons of yarn and it wants to raise it to 20 tons by 2019 and 40 tons by 2020. The company processes around 200 tons of plastic bottles monthly and aims at increasing this figure to 1,000 tons by 2020.
Marty Moran is the new chairman of NCTO for 2018-19. He is a 26-year veteran of the textile sector committed to finding solutions to the challenges facing US manufacturers. The National Council of Textile Organisation represents the entire spectrum of the textile manufacturing sector in the US, from fiber and yarn to fabric and finishing – and everything in between. NCTO strives to bring a clear, strong and aggressive voice of support for US textile manufacturers in the national policy arena.
NCTO is an advocacy organization. Moran will place the highest emphasis on identifying key policy matters that hold the potential to impact the textile sector. He believes if the US textile industry can get customers to focus their business models on actual profit earned rather than on theoretical profit margins on items not yet sold, more textile supply chain jobs and production will be reshored in the United States.
Moran is CEO of Buhler Quality Yarns, a fine-count spinner of premium, innovative and sustainable yarns – most notably Supima, MicroModal and Tencel. Beyond spinning high-quality yarns in the US, Buhler is known for supply chain management, expertise and consultation. In particular, it works with customers to develop nimble, speed-to-market supply chains.
In February 2018, Indian cotton exports were down 13.3 per cent from January, but up 45.2 per cent year on year. Cotton imports were up 37 per cent year on year and up 8.3 per cent month on month. In the first two months of 2018, exports were up 7.2 per cent year on year.
Bangladesh, Pakistan and Vietnam continued to be the major consumers of Indian cotton in February 2018. But exports to Bangladesh were down 17 per cent from January, those to Pakistan were down 34.2 per cent and those to Vietnam were flat from January.
From August 2017 to February 2018, imports were down 46.1 per cent year on year and in the first two months of 2018, imports were up 27.1 per cent year on year. Cotton imports have seen steady growth for four months, which is mainly pushed by the strong demand for quality cotton from Indian spinning mills.
In February 2018, the major cotton suppliers for India were US, Egypt and Mali. US cotton remained the largest volumes, taking a share of 49.14 per cent. Egyptian cotton continued to the second largest import origins, but its proportion declined to 21.44 per cent. Cotton imports have seen steady growth for four months, which is mainly pushed by the strong demand for quality cotton from Indian spinning mills.
Index Dubai fair is being held from March 26 to 29, 2018. The fair features a comprehensive range of furniture, furnishing, decorative accessories, interiors and fittings by a diverse portfolio of 1.000 quality exhibitors from more than 27 countries across Asia and all over the world. A total of 37 Indian companies are participating at this fair, showcasing interiors and decorations, handicrafts, furniture, home furnishing and textiles.
Launched in 1990, Index Dubai is Middle East and North Africa’s largest gathering for the design community. The UAE is one of India’s top trading partners. India and the United Arab Emirates enjoy a strong bond of friendship founded on millennia-old cultural, religious and economic intercourse between the two regions.
Export Promotion Council for Handicrafts (EPCH) is a nodal organization responsible for the promotion of exports of handcrafted products from India to various global destinations and projecting India’s image abroad as a reliable supplier at competitive prices. The India pavilion at the fair was set up by EPCH.
Exports of Indian handicrafts to Dubai were Rs 2757 crores in 2016-17. The hope is that such fairs will give a further boost to Indian handicraft exports to Dubai in the near future.
Swedish fashion retailer Hennes & Mauritz AB has stated that it's increasing markdowns this quarter after accumulating a record pile of unsold garments worth more than $4 billion. Operating profit fell 62 per cent to the lowest level in more than a decade as clearance sales failed to reduce quantities of T-shirts and jeans that customers had passed over.
H&M's already-downbeat forecast for the start of 2018 was exacerbated by unseasonably warm European weather in January followed by February's cold snap, whipsawing the clothing retail industry. That forced the company to slash prices even more. CEO Karl-Johan Persson stated the company made mistakes by narrowing its assortment last year, though he expects sales to improve in the second half.
He further adds that H&M plans to reduce markdowns in the second half, when sales should improve and a weaker dollar will reduce garment costs.
Ethiopia has over 2.4 million hectares of land are suitable for cotton production. And this fiscal, over 40,000 tons of cotton were harvested. The aim is to reach 5,02,000 tons in five years and 2,596,000 tons by 2032.
Ethiopia wants to be the top cotton producer in Africa from tenth place as of now. Sustainable production practices will be promoted through awareness raising campaigns about soil erosion, efficient use of irrigation water and inputs and integrated pest management, protection of biodiversity, forests and limitation of waste.
The strategy would help enhance the development of the country’s textile and garment sector. It is targeted to attain various goals including improving textile and garment products, earning better foreign currency, job creation, utilizing the full potential of industry and increasing the contribution of the industry for GDP. It would also contribute to attracting investments, providing adequate inputs for industries and supplying cotton products for foreign markets.
The strategy would promote integrated value and help bring the cotton sector into the industrialization process and will benefit all stakeholders in general and cotton farmers in particular as it would make them more profitable. An independent entity will be established with authority to coordinate activities by various stakeholders through improving policy and institutional framework.
The US plans to bring a case to the WTO arguing that China is favoring domestic companies for licensing. China has been a big target for cases brought by the US, Japan and the EU, and the US hopes to sign up allies for its planned WTO action.
The EU wants to change WTO rules to permit swifter action against dumping and subsidies. The WTO was founded in 1995 as successor to the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade, forged in 1948. In 2001, the year China joined, members launched talks to update and rewrite global trade rules but those efforts died a decade ago.
Since then, members have cut side deals to open markets. The EU, a vocal champion of free trade and the WTO, has struck or is seeking deals to liberalize trade with Canada, Japan, Mexico, Australia and Singapore. Such bilateral deals are allowed under WTO rules if they are deemed complementary to the multilateral trading system, cover substantially all trade and facilitate the freer commercial flows without raising barriers to non-parties.
US allies say a bigger problem for WTO is that China has taken advantage of the body’s rules to promote itself at the expense of other members. The Geneva-based body was designed before the rise of Chinese state-backed capitalism.