FW
India is pushing for labor-intensive textiles and apparel products to be classified as non-tariff items in the ongoing negotiations for a free-trade agreement (FTA) with the European Union (EU).
This move comes as EU nations currently impose higher import duties, typically ranging from 10-12 per cent, on textile products, putting India at a disadvantage compared to China, the EU's leading supplier of apparel and textiles.
The seventh round of negotiations, which commenced on February 19, holds significant importance for the Indian textiles and apparel sector. This is especially true given that the EU, the US, and West Asian countries are major export destinations for Indian garments.
During the ongoing discussions, the issue of including textiles under the non-tariff barrier category has been prominently raised, signaling optimism among Indian negotiators. India's textile exports to the EU witnessed a decline from $44.43 billion in 2021-22 to $36.68 billion in FY23. In the first 10 months of the current fiscal year, India exported textiles worth $27.69 billion globally, including products valued at $7.67 billion to the EU.
India's emergence as a preferred destination for sourcing textiles, attributed to better quality products adhering to global standards, is seen as a driver for export growth. Stakeholders believe that the elimination of import duties would further stimulate this growth.
However, opinions among experts differ regarding the proposal for zero duty on textile exports. Ajay Srivastava, Founder, Global Trade Research Initiative (GTRI), highlights, merely signing an FTA may not lead to a substantial increase in India’s export of labor-intensive goods. Strengthening the product profile is deemed essential for realising significant gains, as illustrated by India's apparel exports to Japan post the India-Japan FTA, which did not witness the expected surge despite the elimination of duties.

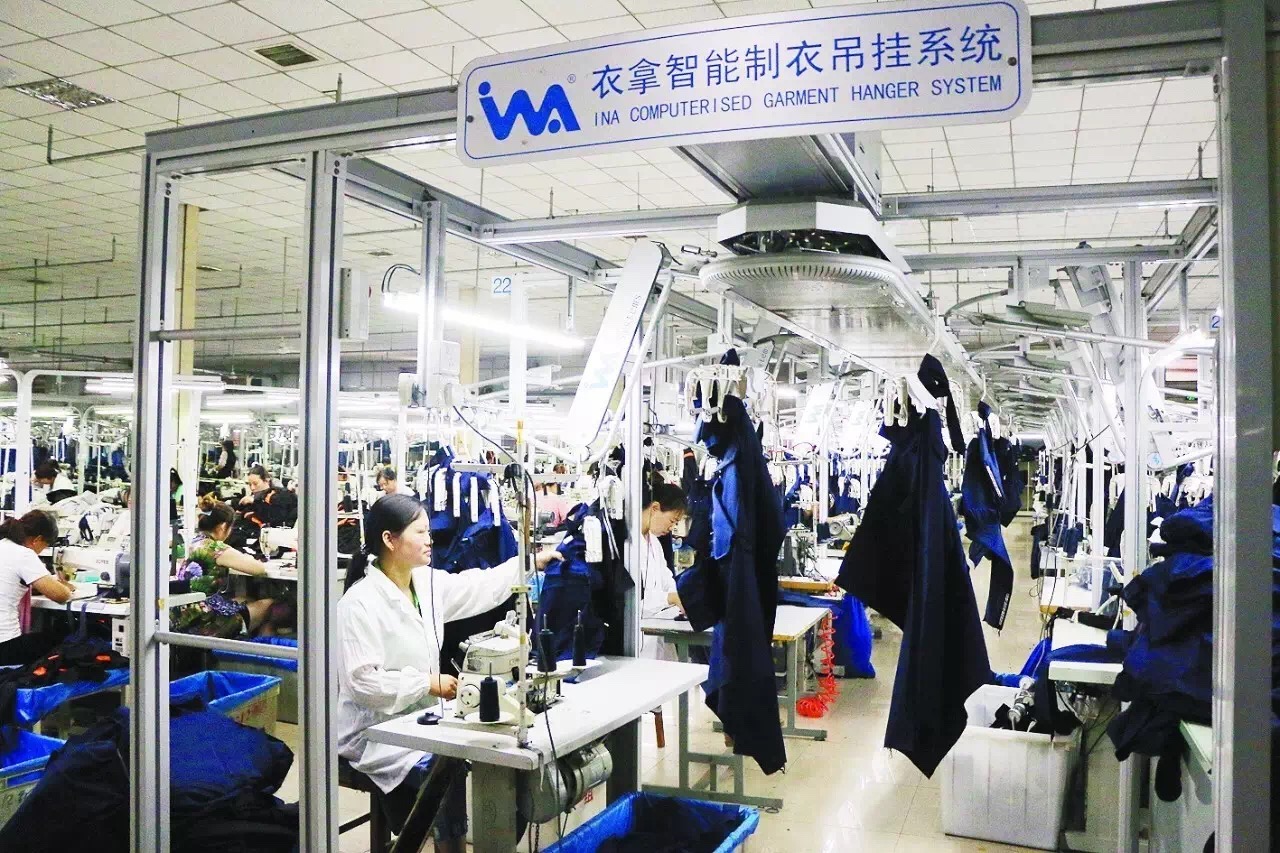
Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the four-day Bharat Tex Expo 2024 at Bharat Mandapam, heralding it as the world's largest textiles event. In his address, PM Modi underscored the government's dedication to integrating all facets of the textile value chain, encapsulated by the strategy of the five F’s: Farm, fibre, factory, fashion, and foreign.
Government's five F’s strategy
PM Modi elucidated on the significance of the five F’s strategy, emphasizing its pivotal role in fostering holistic growth within the textile sector. By aligning efforts towards farm support, fibre development, factory enhancement, fashion promotion, and foreign market expansion, the government aims to bolster the entire spectrum of textile activities. Notably, the recent amendments in the MSME definition regarding investment and turnover seek to empower smaller enterprises, ensuring their access to government initiatives and fostering industry scalability.
Reaffirming the government's unwavering support, PM Modi assured the textiles sector of comprehensive assistance. He reiterated the administration's commitment to augmenting the textile industry's contribution towards India's progress.
Focus on MSME sector
Addressing the Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises (MSME) sector, PM Modi highlighted the series of measures implemented to fortify its foundations. Amendments in the MSME definition aim to bridge the gap between artisans and the market, empowering businesses of all sizes to thrive.
The event witnessed substantial participation, with over 3,000 exhibitors, 3,000 buyers from 100 nations, and approximately 40,000 trade visitors in attendance. This robust engagement underscores the global significance of Bharat Tex Expo 2024 as a premier platform for textile trade and collaboration.
Emphasis on Kasturi Cotton
PM Modi emphasized the role of Kasturi Cotton in shaping India's identity on the global stage. Recognizing India's position as a leading producer of cotton, jute, and silk, he lauded the government's support to farmers and underscored the significance of initiatives like Kasturi Cotton in fostering national pride and sustainability.
Highlighting the textile sector's remarkable growth trajectory, PM Modi noted a 25 per cent increase in the production of yarn, fabric, and apparel over the last decade. This exponential growth reflects the positive impact of stable governance and visionary policies on India's textile landscape, propelling the industry's valuation to over Rs 12 lakh crores.
Bharat Tex 2024: A confluence of trade and investment
Organized by a consortium of 11 Textile Export Promotion Councils and bolstered by government support, Bharat Tex 2024 is positioned as a catalyst for trade and investment in the textile sector. With a strategic focus on sustainability, the event features an extensive lineup of knowledge sessions and global panel discussions aimed at addressing key industry challenges and fostering collaborative solutions.
Bharat Tex 2024 is poised to galvanize investment, trade, and exports in the textile sector, with over 50 announcements and MoUs expected to be signed during the event. By fostering dialogue, innovation, and partnerships, the expo aims to propel the textile sector towards a sustainable and prosperous future.
A showcase of India's textile diversity
Bharat Tex Expo 2024 has designated Uttar Pradesh and Maharashtra as 'Partner States,' recognizing their significant contributions to the Indian textile industry. This acknowledgment aims to underscore the pivotal role these states play in shaping the country's textile landscape. Additionally, the event is set to feature the vibrant textile offerings from Gujarat, Telangana, and Madhya Pradesh, now identified as "Supporting Partner States," further enriching the diversity on display.
The world's largest textiles event, Bharat Tex 2024, serves as a premier platform to exhibit the diverse textile ecosystems thriving across different regions of India. The inclusion of state pavilions from Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Assam adds depth to the showcase, allowing attendees to explore the rich tapestry of India's textile heritage.
Following unsuccessful attempts to secure additional funds amidst sluggish sales over consecutive quarters, pioneering Swedish textile recycler Renewcell announced plans to declare bankruptcy.
Despite expectations to report its full fiscal year earnings, Renewcell later postponed the release amid challenging negotiations with its major shareholders, including H&M and Girindus, along with existing lenders such as BNP Paribas and Nordea. The company failed to attract new investors or devise a viable solution to ensure its ongoing operations.
Renewcell specialises in producing Circulose, a revolutionary textile pulp derived from chemically recycled cotton waste, and operates one of the world's pioneering commercial-scale textile-to-textile recycling facilities.
Renewcell struggled to secure sufficient orders, despite Inditex's commitment to purchase 2,000 tons of material blend made with Circulose through Tangshan Sanyou.
Former CEO Patrik Lundström's departure and the subsequent appointment of Magnus Håkansson as interim CEO marked a transition period aimed at revitalising sales. However, slow sales persisted, prompting renewed appeals to brands to support Circulose adoption.
Renewcell's predicament underscores broader challenges within the fashion industry, where circularity initiatives are hailed as solutions to waste problems, yet implementation remains a hurdle.
H&M's minority stake in Renewcell since 2017 and its endorsement of Circulose material showcased initial optimism. However, despite the full-scale factory's launch in 2022 and ambitious production targets for the future, Renewcell struggled to meet demand and achieve financial viability.
Its bankruptcy announcement reflects the sobering challenges of aligning sustainability aspirations with commercial viability in the fast-paced fashion industry, signaling a setback in the journey towards a circular economy for fashion.

The US economy defied recessionary whispers, growing robustly in Q3 and Q4 2023. This presents both opportunities and challenges for the apparel industry, navigating a "swirl" of economic influences. While interest rates remain a headwind, tailwinds like a strong labor market and rising consumer confidence fuel optimism for the apparel industry. However, key questions linger.
Impact on apparel segments
Rising interest rates could dampen high-end spending, but brand loyalty and exclusivity may offer resilience. With higher disposable incomes and resilient demand, luxury brands are likely to thrive. High interest rates might also nudge some consumers towards pre-owned or vintage luxury, but overall, the segment remains strong.
Price-sensitive consumers might shift towards value options, potentially benefiting fast fashion retailers. Its value proposition and adaptability to trends could attract budget-conscious consumers. Meanwhile, continued focus on health and wellness could drive sustained growth in active wear segment. Consumers increasingly value eco-friendly practices, presenting an opportunity for brands with transparent and sustainable supply chains.
Supply chain considerations
Geopolitical tensions, ongoing labor shortages in key manufacturing regions, and volatile raw material costs could continue to disrupt the apparel supply chain, leading to price fluctuations and delivery delays. Some companies may explore nearshoring or reshoring production to mitigate these risks, although cost considerations and infrastructure limitations remain hurdles. Investments in supply chain transparency and agility can mitigate risks and build resilience. The tight labor market affects apparel manufacturing and logistics. Automating processes, investing in reskilling programs, and offering competitive wages can help address these challenges.
While the Consumer Price Index (CPI) for apparel increased in 2023, retail prices haven't always reflected this. Retailers meanwhile are employing aggressive promotions and discounts to clear inventory and remain competitive. They are offering deeper discounts and promotions to attract price-sensitive consumers, potentially eroding profit margins. In fact, to avoid stockpiles, they may sell existing inventory at lower prices, even as input costs rise. Meanwhile, intense competition in the apparel industry keeps prices down. And to do this, some brands might be substituting cheaper materials to absorb cost increases without raising retail prices significantly.
The way forward
One way to move ahead in a complex economic situation is to diversify product offerings by catering to different price points and a wider range of consumer needs. Offer products that deliver value beyond price, like quality, durability, and unique design. It’s also important to adopt technology and utilize data analytics to optimize inventory management and pricing strategies. Leverage data analytics to understand customer preferences and optimize pricing, marketing. With consumers increasingly drawn to sustainable practices, offering an opportunity for differentiation is also important for brands. Building closer ties with suppliers to mitigate disruption risks and secure reliable sourcing is key. Another important aspect is to adopt omnichannel retail as seamless online and offline experiences are crucial for today's consumers.
Rebounding notably, the comprehensive prosperity index for the China’s textile industry grew by 55.6 per cent, 57 per cent, 55.9 per cent, and 57.2 per cent respectively in 2023, shows data from the China National Textile and Apparel Council.
Capacity utilisation rates and production in the textile sector increased steadily during the year, as per the National Bureau of Statistics. In 2023, the textile and chemical fiber industries boasted capacity utilization rates of 76.4 per cent and 84.3 per ent respectively, surpassing national industrial averages. Particularly, the chemical fiber industry saw a 2-percentage-point increase in utilisation compared to the prior year. Though the industrial added value of large-scale textile enterprises decreased by 1.2 per cent Y-o-Y, it reflected a 0.7 percentage point improvement from 2022.
Diverse and personalised clothing consumption, coupled with the rising popularity of independent brands and the ‘guochao’ phenomenon, fueled domestic demand for textiles. Retail sales of clothing and related goods surged by 12.9 per cent in 2023, marking a 19.4 percentage point increase from 2022, surpassing pre-pandemic levels. Online retail, especially in sporting goods, grew by 10.8 per cent Y-o-Y.
Despite challenges such as reduced overseas demand and increased trade risks, China's textile exports demonstrated resilience. Exports to ‘Belt and Road’ countries showed promise, mitigating overall declines. Total textile and apparel exports reached $293.64 billion in 2023, marking an 8.1 per cent Y-o-Y decrease
While textile enterprises contended with market sluggishness and high costs, improved domestic demand bolstered benefits. Business revenue decreased by 0.8 per cent narrowing by 0.1 percentage points from the previous year, while total profits surged by 7.2 per cent a 32 percentage point increase from 2022. Operating income margins reached 3.8 per cent, a 0.3 percentage point rise from 2022.
Looking to 2024, China's textile industry faces continued uncertainties amid a complex international landscape. Yet, domestic market dynamics driven by urbanisation and ‘guochao,’ along with initiatives like the ‘Belt and Road’ and free trade zones, offer avenues for expansion and resilience against external risks.
Growing at a CAGR of 5.7 per cent, the global technical textile market is poised to reach $331.8 billion by 2032.
As per a report by Textile Today, growth in this market is likely to be driven by the advancements in science and technology, particularly in material science and technology, driving continuous innovation in the sector. Innovations in fiber and fabric technology have led to the creation of high-performance materials boasting attributes such as strength, durability, chemical resistance, and flame retardancy.
In 2024, synthetic polymers/fibers accounted for more than half of the worldwide technical textile market revenue. Synthetic fibers are widely used in automotive, apparel, building, filtration, and home furnishings industries. Woven textiles, categorised by weave, thread density, yarn count, and crimps, dominated the market, contributing to over five-eighths of the revenue.
Rapid urbanisation, population growth, increased construction and remodeling activities, and expansion in the automotive industry are driving market growth. The rise in sales of hybrid and electric vehicles further boosts product demand worldwide.
The healthcare sector contributes significantly to growth of the global technical textiles market with the rise in disposable medical clothing demand and the construction of healthcare facilities globally. Asia-Pacific is expected to rise as the fastest-growing region for technical textiles with growth driven by technological advancements in textile manufacturing.
Demand for industrial textiles is expected to rise during the forecast period, driven by applications in various sectors such as decatising cloth, bolting cloth, drive belts, and printed circuit boards. The growing population in emerging nations fuels demand for sanitary and personal care medical equipment, boosting growth in the medtech textile market.
India’s textile leaders are urging the Central Government to establish a minimum import price (MIP) of $2.71 per kilogram (₹225/kg) for fabric imported from China.
Industry bodies primarily from northern India, particularly Punjab, have warned of suspending production and staging protests starting March 1, 2024, if their demands are not met. This call for action stems from persistent concerns within the textile sector regarding sluggish global demand.
During a meeting convened by the Federation of All Textile Trading Manufacturing Associations (FATTMA) of Ludhiana, industry representatives unanimously agreed to push for an MIP of $2.71 per kg on fabric imports from China. They argued, China has been flooding the market with fabric at significantly reduced prices, alleging that these imports are often under-invoiced. According to them, only by implementing a minimum import price can such practices be curtailed.
A prominent industry leader, Tarun Jain Baba highlighted, they have repeatedly raised these concerns during discussions with officials from the Ministry of Textiles. Indian textile mills have reportedly been compelled to slash their production by as much as 50 per cent of their total capacity.
Business leaders assert that the influx of cheaper fabric is facilitated through the manipulation of the Harmonized System of Nomenclature (HSN) code.
In a collective statement, industry organisations have issued an ultimatum to the government, warning of a complete halt in production across various sectors including spinning, weaving, knitting, dyeing, and printing if their demands are not addressed promptly.
In 2023, China’s cotton yarn imports from Pakistan surged by 46.7 per cent to a record high of $695.62 million, as per reports by the China Chamber of Commerce for Import and Export of Textile and Apparel (CCCT).
In its recent report, the All Pakistan Textile Mills Association (APTMA) attributed this import surge to a sharp rise in energy prices coupled with interruptions in power and gas supply which led to over a thousand textile factories halting production.
According to CCCT, the import surge was a result of the substantial price gap between domestic and foreign cotton yarns, particularly evident after the second quarter of the year. This discrepancy motivated importers to increase their orders, further driving up imports.
In December 2023, China’s cotton yarn imports from India, Pakistan, and Uzbekistan increased substantially by 243.2 per cent 351.1 per cent, and 867.1per cent, respectively. Its cotton yarn imports from Pakistan alone accounted for 15.8 per cent of China’s total imports in this category throughout the year.
As per statistics from the General Administration of Customs of China (GACC), the total value of yarn imports and exports in 2023 amounted to $19.68 billion, reflecting a 2.9 per cent decrease compared to the previous year. While exports declined by 8.6 per cent to $13.7 billion, imports rose by 13.2 cent to $5.98 billion.
Import quantities also increased by 32.6 per cent to 2.043 million tons.
Cotton yarn remains a crucial category among China's yarn imports, constituting 70 per cent of the total and representing 24 per cent of textile and clothing imports.
The demand for imported cotton and cotton yarn in China shows no signs of slowing down, with cumulative imports reaching 1.687 million tons in 2023, marking a significant 43.4 per cent increase compared to the previous year.
While Australian wool auction results remained mostly unchanged last week, with some softening in Western Australia, measured in US dollars (USD), the market saw a 1.3 per cent increase in the Eastern Market Indicator (EMI). This reflects a slightly stronger demand considering the global wool trade primarily uses USD.
Following the Chinese New Year break, activity in the Australian wool market picked up as businesses resumed operations. While direct buyers and some traders showed increased participation, European operators remained cautious, according to a report by the Australian Wool Innovation (AWI) report.
Demand for Merino Wool (19-22 microns) continued to rise leading to a slight rise in prices. However, prices of super fine wools declined.
Prices of finer and broader micron crossbred wools also declined while those of mid-micron types remained stable due to stronger exchange rates. Carding Wool prices held firm, with some sectors even witnessing slight increases.
This week, the market anticipates 40,000 bales offered, indicating continued activity.
The International Cotton Advisory Committee's (ICAC) Task Force on Commercial Standardization of Instrument Testing of Cotton (CSITC) has achieved a remarkable decade-long streak of improvement in Round Trials (RTs), spanning from 2011 to 2023. This continuous success underscores a crucial commitment to accuracy and consistency within the cotton industry.
In the latest 2023 RTs, involving laboratories from 30 countries, between 57 and 68 labs participated in each of the four trials. Despite seasonal fluctuations, the number of instruments tested ranged from 90 to 158, with the third RT of 2023 nearly breaking the all-time record set in 2012. The average annual median Overall Evaluation Result (OER) in 2023, standing at 0.342, remains commendable, although slightly below the peak achieved in 2021.
The significance of these results extends beyond numerical achievements. Over the past decade, participating labs have consistently reduced variation across key properties such as Micronaire, Strength, and Length Uniformity, among others. This trend is exemplified by the substantial improvement in the median OER, which has decreased from 0.54 in 2010 to 0.34 in 2023, as illustrated in the accompanying chart.
These advancements not only enhance the reliability of instrument testing but also foster trust and integrity within the global cotton trade. By ensuring accurate measurements and minimizing discrepancies, the ICAC's CSITC initiatives contribute to smoother transactions, reduced disputes, and overall efficiency in the industry.
Since 2007, CSITC RTs, managed by ICAC, organized and evaluated by Bremen Fibre Institute, and facilitated by USDA for sample provisions and dispatch, have been conducted quarterly. The objective is to align lab results with reference values, reducing inter-laboratory deviation to mitigate costly claims for buyers and sellers.